InspeçãoRobótica
In-Pipe CrawlersInspeção de tubos não pigáveis
O desafio
Vazamentos, rachaduras e defeitos internos em tubulações, estruturas, espaços confinados e outros ativos são problemas comuns na área de inspeção do setor de energia.
Novas tecnologias de testes não destrutivos são aplicadas para prever e avaliar esses problemas.
Nossa solução
Para atender à crescente demanda do setor de energia por ferramentas de inspeção inteligentes, a ouronova oferece uma família de robôs modulares operados remotamente que podem realizar várias técnicas de inspeção não destrutiva (NDT).
Diferentes tipos de testes de avaliação podem ser realizados em uma única operação. A ouronova fornece robôs e serviços de inspeção, incluindo relatórios de integridade sobre a condição física dos ativos, minimizando o tempo e os recursos gastos em reparos.
Tatuí | Simas | Simão | |
|---|---|---|---|
ID Range | 2.5” to 5” | 6” to 15” | 14” to 25” |
Visual | |||
Wall thickness | |||
ToFD | |||
MFL | |||
Geometric |
Tatuí
Tatuí
O TATUÍ foi projetado para uso em tubulações não pigáveis de diâmetro entre 2,5” e 5”, focando principalmente na demanda por risers de perfuração.
Pode operar sem pressão de fluxo na tubulação, utilizando seu próprio sistema de acoplamento. O sistema de locomoção autoajustável permite inspecionar tubulações de múltiplos diâmetros em qualquer direção, gerando e registrando imagens e dados em tempo real.
Vantagens
- Unidade bidirecional com controle de velocidade e posição
- Gravação e visualização de imagens em tempo real
- Sistema de locomoção autoajustável para múltiplos diâmetros
- Avaliação da espessura da parede
- Autopropulsão utilizando motores elétricos
Tatuí
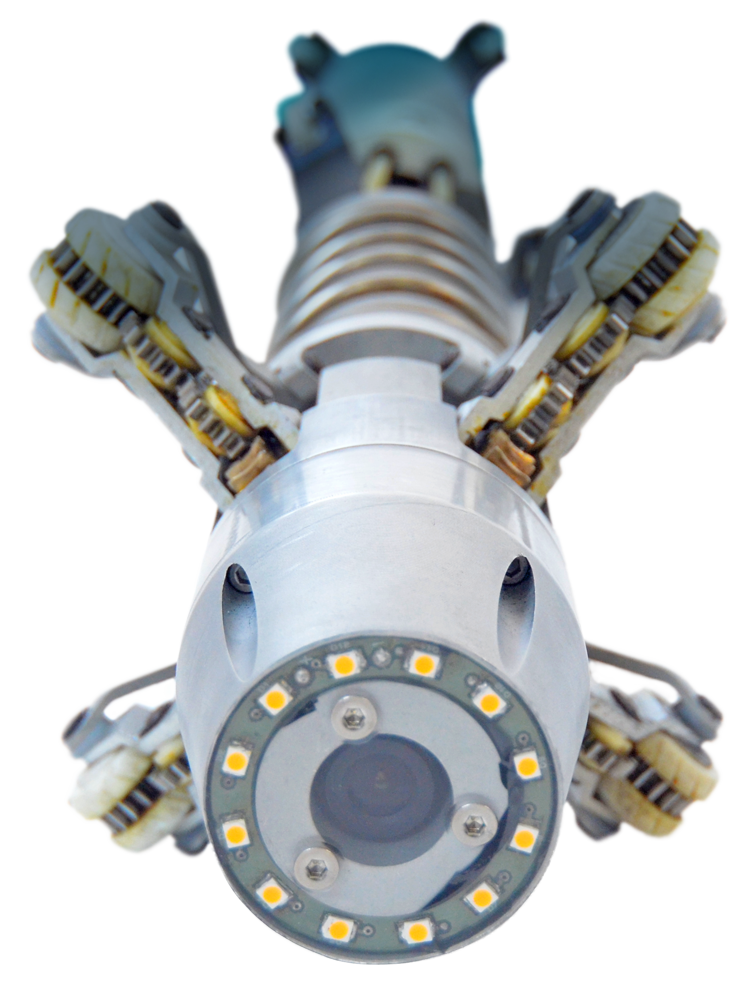
Simas
Simas
Simas
Este sistema robótico realiza inspeções visuais e mede a altura da penetração da raiz de soldas e estruturas tubulares entre 6″ e 15″.
O robô possui uma câmera de alta definição com movimento de pan/tilt e projeção a laser. Com sua própria tecnologia de processamento de imagem (com uma incerteza de 0,03 mm na medição de altura), o SIMAS pode ser usado para inspeções visuais de tubulações lineares e curvas, incluindo inclinações.
Assim como sua versão maior, é modular e pode ser acoplado a vários módulos, como ultrassom, geométrico e raio gama.
Vantagens
- Inspeção visual remota - pode ser em uma região específica ou 360°
- Inspeção e medição da altura da penetração da raiz da solda
- Inspeção e medição de descontinuidades
- Inspeção e medição da profundidade e comprimento de sulcos
- Todas as inspeções podem ser gravadas com vídeos e imagens em alta definição

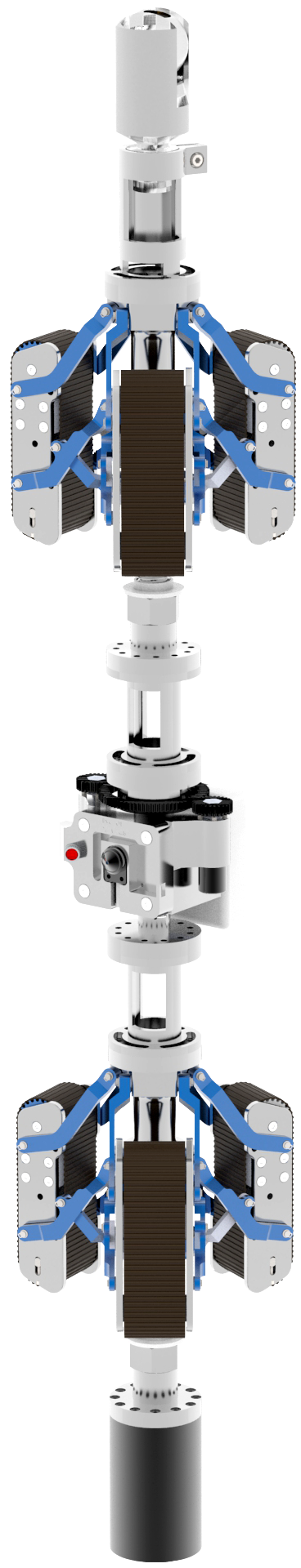
Simão
Simão
Este robô possui controle remoto de velocidade e posição, além de visualização e gravação de dados em tempo real via umbilical.
As principais características deste equipamento são a versatilidade e a modularidade. É uma solução poderosa e inovadora para testes não destrutivos (NDTs). O SIMÃO utiliza uma variedade de módulos de exames não destrutivos (NDE).
Vantagens
- Módulo de ultrassom ToFD para realizar inspeções de soldas e equipamentos
- Módulo MFL para realizar inspeções de integridade de tubulações e estruturas
- Módulo geométrico para detecção de ovalidade e outras anomalias geométricas
- Módulo de ultrassom para medição de espessura de parede
- Módulo visual com câmera PTZ (Pan/Tilt/Zoom) de alta resolução
- Outros módulos podem ser desenvolvidos e acoplados ao robô
Simão
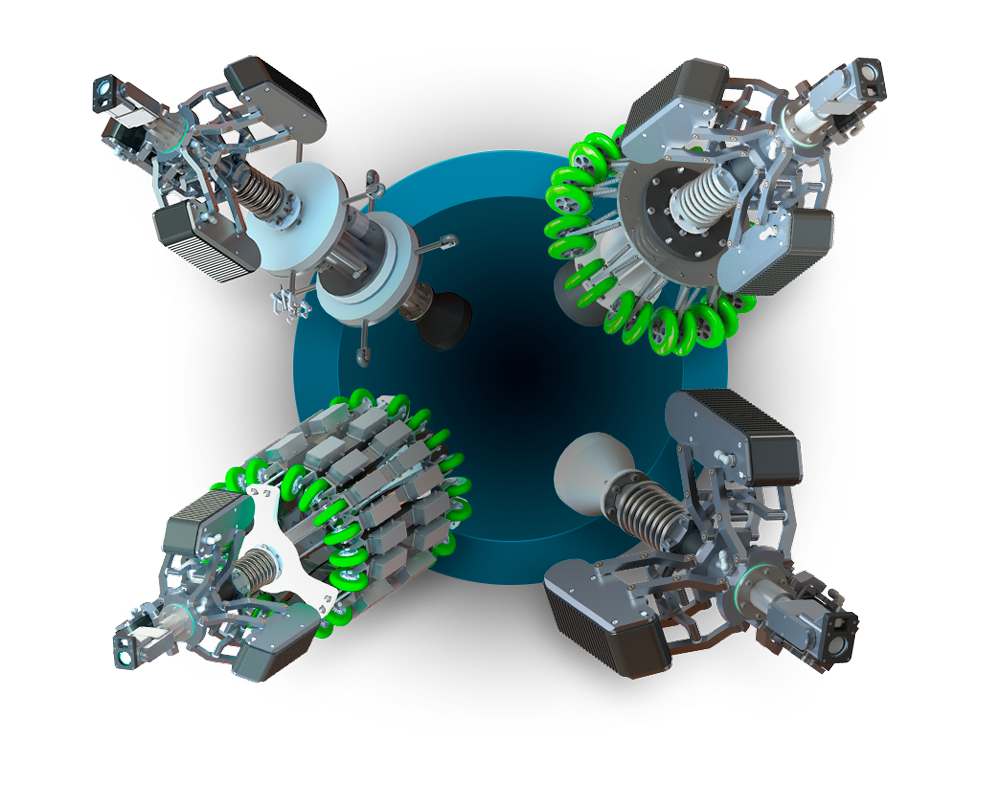
Entre emContato
Preencha suas informações corretamente e entraremos em contato em breve.
Artigos
Abstract
Welding of submarine tubular structures is often a challenge for the company responsible for this task. This process must attend highly stringent standards and it is subject to various inspections to verify the compliance. Failure to comply with the standards results in reworking and, sometimes, the definitive loss of part of the structure, generating costs for the producing companies and to the executors. Once the root of the weld and the first filling layers are made, the robot is used for internal visual inspection and for measuring the height of penetration of the root of the weld. If the root of the weld presents excessive penetration (a failure to comply with the standard), the robot is able to analyze the penetration height and inform the inspector in real time. This paper presents the steps of developing a robotic vehicle to perform weld inspections of underwater tubular structures and non-piggable pipes, as well as their field tests and results
Abstract
Oil and gas drilling riser integrity has been a big concern of drilling companies for decades.Techniques used to evaluate riser integrity so far require transporting drilling risers for onshoreinspection, which generates significant logistics costs. This paper describes the developmentand evaluation of a robotic tool for offshore internal drilling riser inspection, in order to reducecosts. A hierarchical assessment methodology is proposed, where magnetic flux leakage (MFL)magnetizer and sensors are used in addition to a high-resolution camera to detect riser sectionswith a higher probability of defects such as wall thickness loss. An ultrasound probe is then positioned at the identified area to provide a more detailed analysis. This unique combinationis made possible by designing a system actuated by electrical motors, which positions both theMFL sensors and the ultrasonic probe at the same precise point to enhance the desiredassessment. The MFL magnetizer module is designed with Finite Elements to properlymagnetize the section of interest while keeping the weight as low as possible to be carried bythe robot. Multiple magnetizer configurations adapt tool to target wall thickness of the risersection, enabling a lightweight customized MFL sensor to map areas for further ultrasoundinspection. Prototype test results on a standard drilling riser with known defects are presentedin this work and evaluate the system’s ability to detect the presence of a defect as well as the precision at measuring its size. Results show that the proposed methodology has higher performance when detecting and measuring defects when compared to normative requirements.
Abstract
The motivation for this project was the resumption of construction of the Gasfor II gas pipeline. This project aimed to develop an autonomous robotic system capable of carrying a Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) inspection tool along pipeline sections with an external diameter of 20 inches, without fluid flow, with various curves and inclinations, and with a maximum length of 5 km. The project started considering the SIMÃO inspection robot and an existing MFL tool, but it was soon verified during initial tests that the necessary payload for using the tool would be much higher than the current payload capacity of the SIMÃO robotic system. Another motivating factor for the development of the autonomous system was the impossibility of using a power supply cable due to the significant voltage drop along 5 km and also due to the cable drag in the curves.The system was developed by the companies ouronova and Pipeway and tested during the construction of the TAG Gasfor II pipeline with the support of the company Norteng.
Abstract
Welding of submarine tubular structures is often a challenge for the company responsible for this task. This process must attend highly stringent standards and it is subject to various inspections to verify the compliance. Failure to comply with the standards results in reworking and, sometimes, the definitive loss of part of the structure, generating costs for the producing companies and to the executors. Once the root of the weld and the first filling layers are made, the robot is used for internal visual inspection and for measuring the height of penetration of the root of the weld. If the root of the weld presents excessive penetration (a failure to comply with the standard), the robot is able to analyze the penetration height and inform the inspector in real time. This paper presents the steps of developing a robotic vehicle to perform weld inspections of underwater tubular structures and non-piggable pipes, as well as their field tests and results.
Abstract
Oil and gas drilling riser integrity has been a big concern of drilling companies for decades. Techniques used to evaluate riser integrity so far require transporting drilling risers for onshore inspection, which generates significant logistics costs. This paper describes the development and evaluation of a robotic tool for offshore internal drilling riser inspection, in order to reduce costs. A hierarchical assessment methodology is proposed, where magnetic flux leakage (MFL) magnetizer and sensors are used in addition to a high-resolution camera to detect riser sections with a higher probability of defects such as wall thickness loss. An ultrasound probe is then positioned at the identified area to provide a more detailed analysis. This unique combination is made possible by designing a system actuated by electrical motors, which positions both the MFL sensors and the ultrasonic probe at the same precise point to enhance the desired assessment. The MFL magnetizer module is designed with Finite Elements to properly magnetize the section of interest while keeping the weight as low as possible to be carried by the robot. Multiple magnetizer configurations adapt tool to target wall thickness of the riser section, enabling a lightweight customized MFL sensor to map areas for further ultrasound inspection. Prototype test results on a standard drilling riser with known defects are presented in this work and evaluate the system’s ability to detect the presence of a defect as well as the precision at measuring its size. Results show that the proposed methodology has higher performance when detecting and measuring defects when compared to normative requirements.
Abstract
Welding of submarine tubular structures is often a challenge for the company responsible for this task. This process must attend highly stringent standards and it is subject to various inspections to verify the compliance. Failure to comply with the standards results in reworking and, sometimes, the definitive loss of part of the structure, generating costs for the producing companies and to the executors. Once the root of the weld and the first filling layers are made, the robot is used for internal visual inspection and for measuring the height of penetration of the root of the weld. If the root of the weld presents excessive penetration (a failure to comply with the standard), the robot is able to analyze the penetration height and inform the inspector in real time. This paper presents the steps of developing a robotic vehicle to perform weld inspections of underwater tubular structures and non-piggable pipes, as well as their field tests and results.